
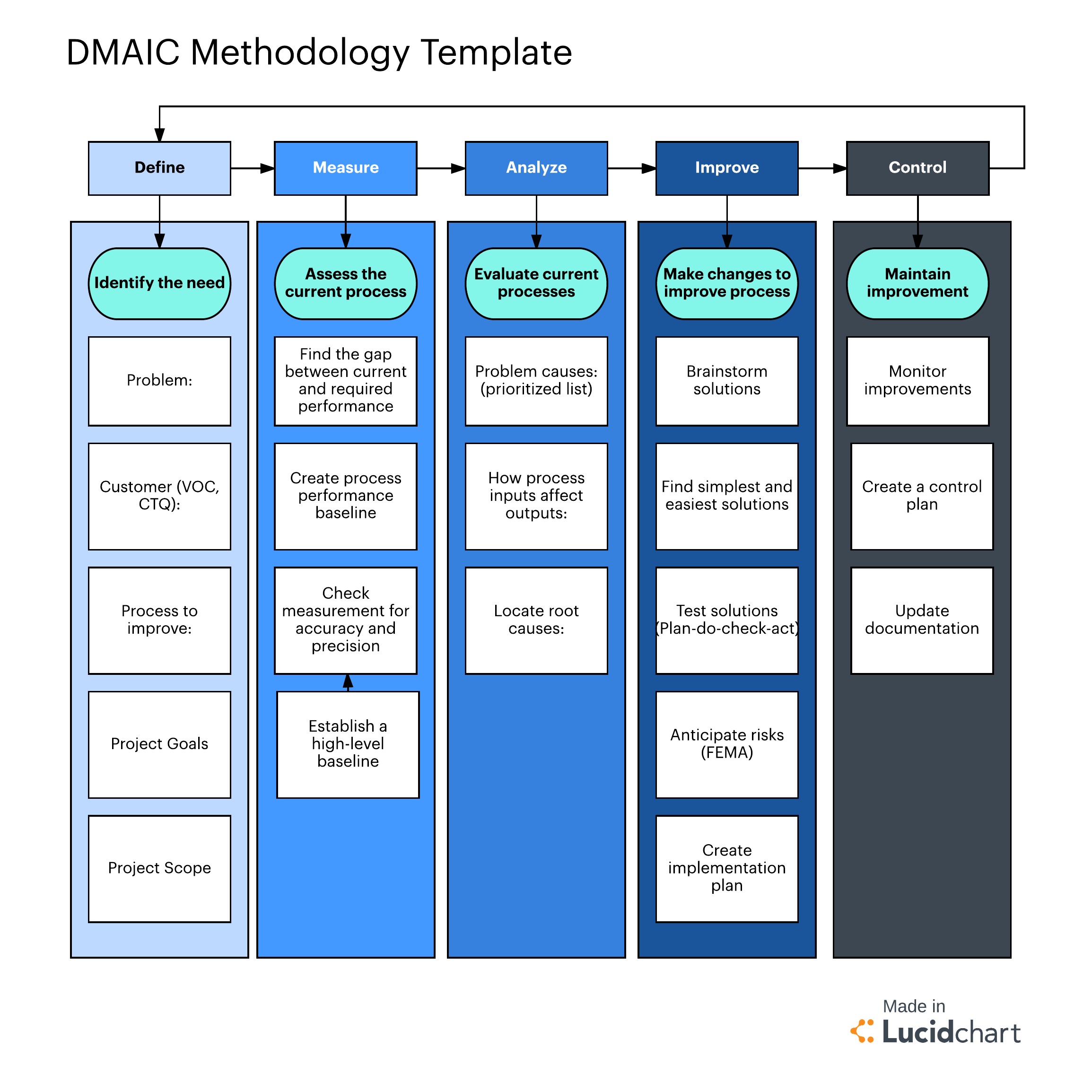
The following links cover topics that are often applied within the ANALYZE phase:Īnalyzing the sources of Process Variation:Īlpha and Beta Risks (Type I Error and Type II Error)Īt this point in the project, and perhaps earlier in the MEASURE phase, there were delays or encounters of adversity. The outputs of ANALYZE lead into the inputs to the IMPROVE phase.
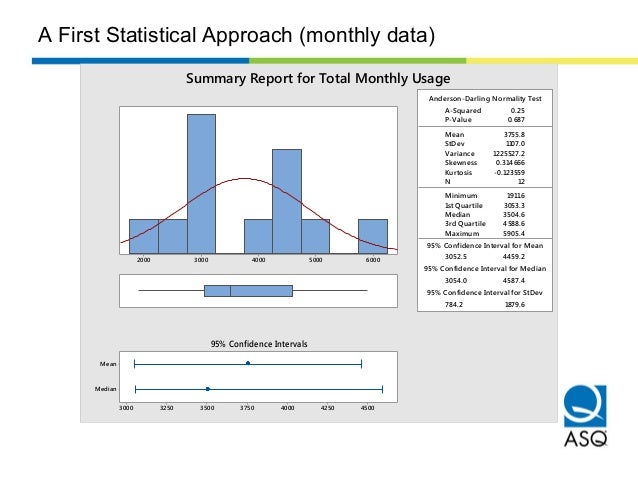
Any wastes found by employing Lean tools should be identified and prioritized to improve. By the end of the ANALYZE phase the KPIV's that are creating the most significant effect on "Y" should be identified. With its data-driven approach, Six Sigma has been widely. This phase is about statistically comparing means and variation on all families of variation to drill down and quantitatively explain the critical sources of the dispersion. Six Sigma is a process improvement methodology that aims to eliminate defects in any process. TOTAL VARIATION = PROCESS VARIATION + MEASUREMENT SYSTEM VARIATION Most of the analysis at this phase is not whether the AFTER process performance is different than the BEFORE process performance because none of the improvements have been implemented yet, these improvements are now becoming evident and prioritized. The remaining variation is Process Variation. By now the MSA has been accepted and the Study Variation has been quantified. For example: You may analyze part-part variation, shift-shift variation, operator-operator variation, machine-machine variation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
